Understanding Ankle Pain Shooting Up the Leg: Treatment
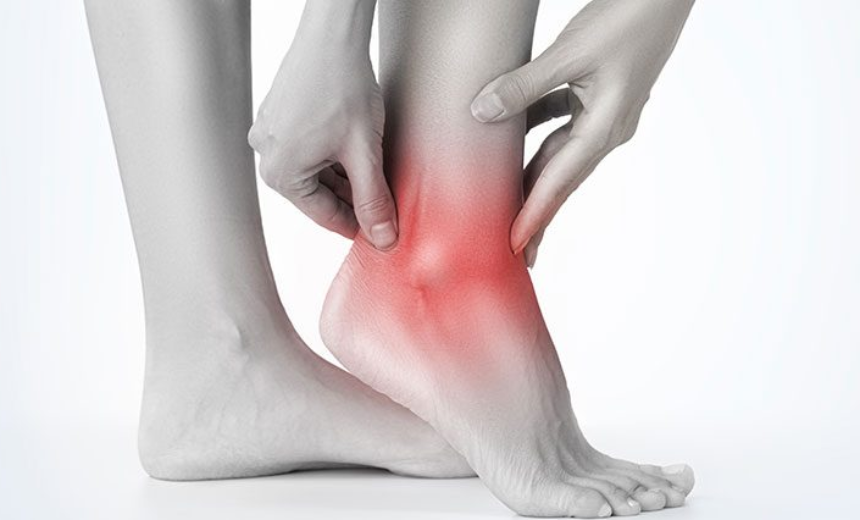
Ankle pain that shoots up your leg can be debilitating and concerning. Understanding the causes, treatment options, and recovery process is crucial for anyone experiencing this discomfort. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into ankle tendonitis, its causes, and how to find the right care.
What Is Ankle Tendonitis?
Ankle tendonitis is a condition characterized by shooting pain from the ankle up the side or back of your leg. This pain is often accompanied by stiffness in the joint, swelling in the ankle, and discomfort in the back of the ankle. The condition primarily affects the two tendons that provide support to the ankle and extend up the leg behind the fibula bone.
Causes of Ankle Tendonitis
Ankle tendonitis doesn’t always result from a single traumatic incident. Instead, it frequently develops gradually due to various factors, including:
- Poor Choice of Footwear
Wearing inadequate or unsupportive footwear can contribute to the development of ankle tendonitis.
- Repetitive Stress
Activities that involve repetitive stress on the ankle, such as jogging or running, can strain the tendons over time.
- Overuse
Excessive use of the ankle without adequate rest can lead to overuse injuries like tendonitis.
- Sudden Increase in Exercise
A sudden and significant increase in exercise intensity or duration can strain the ankle tendons.
- Incorrect Training Techniques
Improper positioning or training techniques during physical activities can increase the risk of tendonitis.
- Previous Injuries
Individuals with a history of ankle injuries, such as sprains, tears, or contusions, may be more susceptible to ankle tendonitis.
- Foot Structure
Foot anatomy plays a role in the development of tendonitis. People with unusually high arches or flat feet are at a higher risk.
- Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions characterized by inflammation, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout, can predispose individuals to ankle tendonitis.
Treatment for Ankle Tendonitis
If you suspect ankle tendonitis, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial. An experienced physician will conduct a thorough examination and may recommend diagnostic tests such as ultrasound or X-ray to assess the extent of the injury.
Treatment options for ankle tendonitis include:
- Rest, Ice, Elevation, and Compression. Initial management often involves rest, applying ice to reduce inflammation, elevating the affected leg, and using compression bandaging;
- Physical Therapy. Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the ankle and promote healing;
- Orthopedic Inserts. In cases related to foot structure, orthopedic inserts to support the arch of the foot may be prescribed;
- Supportive Footwear. Physicians may recommend supportive shoes designed to alleviate strain on the ankle;
- Surgical Intervention. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged tendons. Recovery from surgery may involve a period of non-weight-bearing on the affected foot.
Recovery Duration
The recovery period for ankle tendonitis varies from person to person. While most individuals can expect to fully recover within one to two months by following medical advice, it’s essential to be patient and not rush the healing process. Compliance with treatment recommendations is critical.
Table: Comparison of Treatment Options for Ankle Tendoniti
| Treatment Option | Description | Expected Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE) | Initial treatment involves rest, ice to reduce swelling, compression bandaging, and elevation to alleviate pain and promote healing. | Varies, typically several weeks |
| Physical Therapy | Rehabilitative exercises and techniques prescribed by a physical therapist to strengthen ankle muscles and improve flexibility. | Several weeks to months |
| Orthopedic Inserts | Customized or over-the-counter inserts designed to provide support and improve alignment, particularly for individuals with flat feet. | Ongoing support |
| Footwear | Choosing supportive shoes with proper arch and ankle support to reduce strain on the tendons. | Ongoing as part of daily routine |
| Surgical Intervention | In severe cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to repair or reconstruct damaged tendons. | Six to eight weeks without weight-bearing |
Prevention and Lifestyle Adjustments
Preventing ankle tendonitis and reducing the risk of recurrence involves making some lifestyle adjustments and adopting protective measures. Here are some key strategies:
- Proper Footwear: Invest in shoes that provide adequate arch support and cushioning, especially if you have high arches or flat feet. Well-fitting footwear can reduce the strain on your tendons during physical activities;
- Gradual Exercise Progression: When starting a new exercise or training program, ease into it gradually. Avoid sudden, intense increases in activity levels that can put excess stress on your ankles;
- Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Always warm up before exercise and cool down afterward. Stretching exercises can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury;
- Strength Training: Incorporate ankle-strengthening exercises into your routine. Building up the muscles around your ankles can provide added support and stability;
- Proper Technique: If you participate in sports or activities that involve repetitive movements, ensure you’re using proper techniques to minimize the risk of overuse injuries;
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any signs of discomfort or pain in your ankles. If you experience persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare professional promptly;
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can increase the risk of muscle cramps and injuries. Stay well-hydrated, especially during physical activities.
By taking these preventive measures and making lifestyle adjustments, you can reduce the likelihood of developing ankle tendonitis and enjoy an active, pain-free life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ankle tendonitis is a painful condition that can significantly impact your daily life and physical activities. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for prompt and effective management. If you suspect ankle tendonitis, seek medical attention to determine the extent of the injury and receive appropriate care.
With the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments, most individuals can fully recover from ankle tendonitis and minimize the risk of recurrence. Remember, early intervention and proper care are key to a smoother and faster recovery process.
FAQ
Common symptoms include pain in the ankle that may shoot up the leg, stiffness in the joint, swelling around the ankle, and difficulty walking or running.
Ankle tendonitis is often caused by factors such as poor footwear, repetitive stress from activities like jogging, overuse, sudden increases in exercise intensity, incorrect training techniques, and previous ankle injuries.
Diagnosis involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional. In some cases, imaging tests like ultrasounds or X-rays may be used to determine the extent of the injury.
Treatment options range from rest, ice, elevation, and compression bandaging for mild cases to surgical intervention in severe cases. Physical therapy and orthopedic inserts may also be recommended.