Understanding Hypertensive Crisis: High Blood Pressure
Disclaimer: Information is provided for informational purposes only. It cannot replace a doctor’s consultation.
Although it is a serious health problem, not all cases of high blood pressure require hospitalization. It is important to know when it is high enough to require emergency care.
When Does High Blood Pressure Become a Medical Emergency?
When you need urgent medical attention:
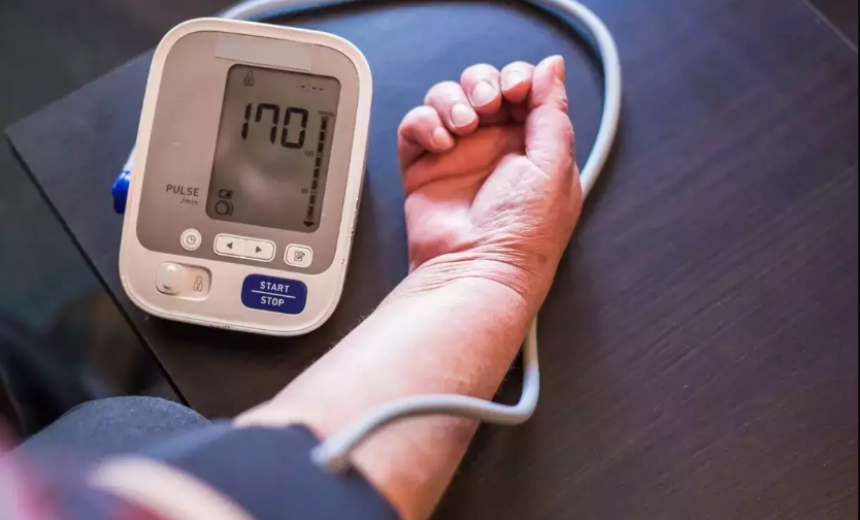
- Pay close attention to signs of elevated blood pressure: In addition to hypertension (180/120 and higher), be vigilant for accompanying symptoms such as severe headaches or chest pain, shortness of breath, blurred vision, confusion, seizures, or signs of organ failure. If any of these symptoms indicate a hypertensive crisis, seek immediate medical assistance;
- Inability to respond to medication: If you have been diagnosed with hypertension and are taking medication but your blood pressure remains dangerously high despite taking prescribed doses, seek urgent medical attention. This may indicate a serious underlying issue or resistance to medications;
- Watch for signs of organ damage: Do not delay seeking medical help if you experience symptoms such as chest pain (indicating heart damage), a sudden severe headache (possible brain damage), difficulty breathing (lung damage), or severe abdominal pain (kidney damage).
Individuals with long-standing uncontrolled hypertension are at risk of developing complications such as aortic dissection (a tear in a large artery), stroke, heart attack, or kidney failure. If there is suspicion of any of these complications, immediate medical attention is essential.
What to Expect During Hospitalization
When you are admitted to the hospital due to elevated blood pressure, you can anticipate a comprehensive and carefully managed approach to your care. Here’s an in-depth look at what you can expect:
- Thorough Evaluation: Your primary healthcare provider will conduct a thorough examination, which includes measuring your blood pressure and assessing your overall health. Expect questions about your medical history, current medications, and any symptoms you might be experiencing. This comprehensive evaluation helps the medical team tailor your treatment plan to your specific needs;
- Medication Management: In the majority of cases, your healthcare provider will prescribe medications either orally or through intravenous administration to lower your blood pressure promptly. The choice of medication and treatment strategy will be determined based on the severity of your condition and your individual health profile. It’s essential to follow your prescribed medication regimen diligently;
- Continuous Monitoring: Throughout your hospital stay, you will receive continuous monitoring to ensure that your blood pressure stabilizes and that you do not encounter any further complications. Monitoring may involve regular blood pressure measurements, heart rate checks, and assessments of organ function to guarantee your well-being;
- Specialized Treatment: If there are indications of organ damage or severe complications related to your elevated blood pressure, you may require specialized treatment. This could involve surgical interventions or organ-specific procedures designed to address and manage the specific issues arising from your condition.
Your health is the top priority during your hospitalization, and the medical team will work diligently to provide the best care possible. Timely intervention and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan are crucial factors in ensuring a positive outcome.
Preventing High Blood Pressure Emergencies
There are several measures that can be taken to prevent emergencies related to high blood pressure, including:
- Blood Pressure Management: If you have high blood pressure, it’s essential to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that includes lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medication;
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: The risk of high blood pressure can be increased by excess body weight or obesity;
- Follow a Healthy Diet and Engage in Physical Activity: Diets low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium can help lower blood pressure. Regular physical activity, with at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise several days a week, is also beneficial;
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to elevated blood pressure;
- Quit Smoking Completely: Smoking can damage blood vessels and worsen hypertension.
Discuss your concerns about blood pressure with your doctor. They can help you develop a blood pressure management plan and reduce the risk of emergencies related to high blood pressure.
Conclusion
In critical moments like a hypertensive crisis, emergency departments play a pivotal role in delivering swift and efficient care to patients. It’s crucial to recognize that your health takes precedence, and making timely decisions can have a profound impact on your overall well-being.
- Comprehensive Assessment: When you arrive at the emergency department, a team of healthcare professionals will conduct a thorough evaluation of your condition. This includes a careful assessment of your blood pressure, overall health, and any concerning symptoms you may be encountering. Your medical history and current medications will also be considered to tailor the treatment plan to your unique needs;
- Medication Management: In most cases, you can expect the administration of medications either orally or intravenously to swiftly lower your blood pressure. The selection of medications and the treatment approach will be determined by the severity of your hypertensive crisis. It’s essential to adhere to the prescribed medication regimen to optimize your response to treatment;
- Continuous Oversight: Throughout your stay in the emergency department, healthcare providers will maintain close monitoring to ensure the stabilization of your blood pressure and prevent any potential complications. This involves frequent blood pressure measurements, heart rate monitoring, and assessments of organ function to safeguard your health;
- Specialized Care: If signs of organ damage or severe complications arise due to your hypertensive crisis, specialized interventions may be necessary. These interventions can encompass surgical procedures or organ-specific treatments designed to address and manage the specific issues associated with your condition.
Your health journey in the emergency department is guided by a commitment to providing you with the best possible care. Rapid and appropriate action, coupled with your cooperation in following the treatment plan, are key factors in achieving a positive outcome. Remember, when it comes to your health, every moment counts.